Regular vs. Irregular Verbs in English: What’s the Difference
Regular vs. Irregular Verbs in English: What’s the Difference
When learning English, one of the key challenges is understanding how verbs work, especially when it comes to regular and irregular verbs. These two categories can confuse many learners, but once you understand the difference between them, using them correctly becomes much easier.
In this article, we will explore the distinction between regular and irregular verbs, give you practical examples, and provide exercises to help you master both. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to improve your English skills, this guide will help clarify any confusion and boost your confidence in using verbs correctly.
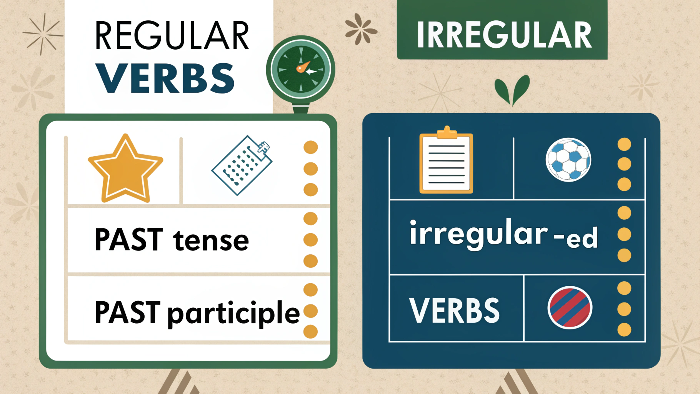
What Are Regular Verbs
Regular verbs are verbs that follow a standard pattern when changing from the present tense to the past tense. Specifically, regular verbs form their past tense and past participle by adding -ed to the base form of the verb.
Examples:
Work → Worked
Play → Played
Talk → Talked
Jump → Jumped
Rule to Remember:
For most regular verbs, you simply add -ed to the base verb. However, there are a few small spelling rules to keep in mind:
If the verb ends in -e, just add -d (e.g., love → loved).
If the verb ends in a consonant + -y, change the -y to -i and add -ed (e.g., cry → cried).
What Are Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs are verbs that do not follow a consistent pattern when changing from the present tense to the past tense. These verbs can change in various ways, and often you need to memorize their past forms.
Examples:
Go → Went
Eat → Ate
Take → Took
See → Saw
Come → Came
Key Point:
Irregular verbs don’t follow the -ed rule. Instead, their past forms must be memorized. These verbs can change in unpredictable ways, so it’s important to learn and practice them regularly.
Regular vs. Irregular Verbs: Key Differences
| Aspect | Regular Verbs | Irregular Verbs |
|---|---|---|
| Past Tense Formation | Add -ed to the base form of the verb. | Do not follow a consistent pattern; the past form must be memorized. |
| Examples | Talk → Talked, Walk → Walked | Go → Went, Eat → Ate |
| Common Usage | More predictable and easier for beginners to learn. | Used frequently in everyday language, but harder to learn due to irregular patterns. |
Common Regular Verbs and Their Past Forms
Let’s take a closer look at some common regular verbs and their past tense forms:
Play → Played
Study → Studied
Work → Worked
Visit → Visited
Look → Looked
These regular verbs are straightforward. To change them to the past tense, simply add -ed.
Common Irregular Verbs and Their Past Forms
Now, let’s examine some common irregular verbs. As mentioned, the past forms of these verbs don’t follow a pattern, so you will need to memorize them:
Be → Was/Were
Begin → Began
Do → Did
Go → Went
Have → Had
Here’s a helpful tip: You can find lists of the most commonly used irregular verbs and study them regularly.
Regular vs. Irregular Verbs in English: What’s the Difference
For more, go to the next page